How is the sharpener being made?
A visual study of the manufacturing methods & tools required to make a sharpener
Groupmates with Jieying, Mariel and Jocelyn | 13 weeks project, a few days outcome using GIFs and CADs, 2017
It was a fun project, lol

Product teardown of a sharpener

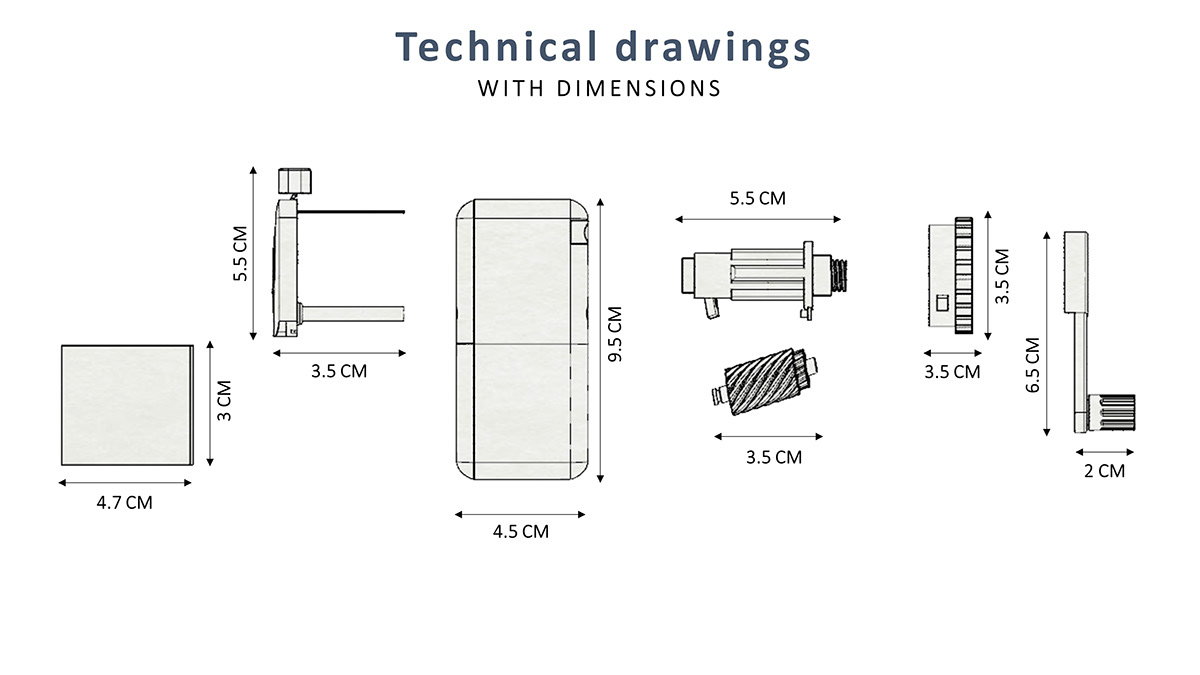

PROCESS 01: Cold Rolling
After hot rolling the steel, it is cooled, before re-rolling it at room temperature.
Advantages
In order to achieve exact dimensions and better and smoother surface qualities for better aesthetics. The steel hardness, resistance against tension breaking and resistance against deformation are increased.
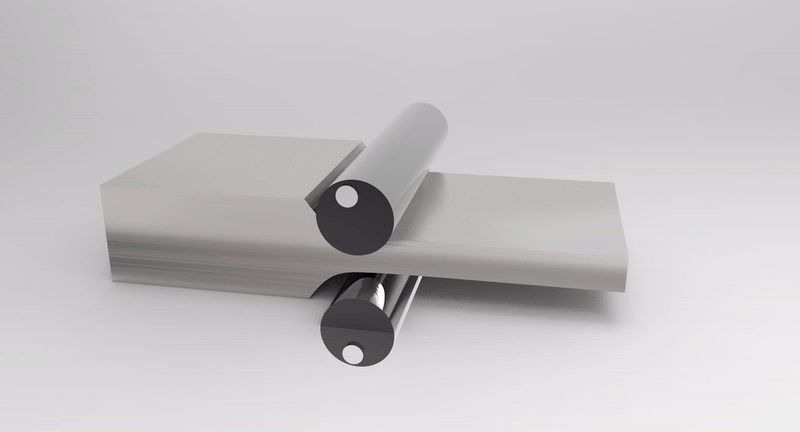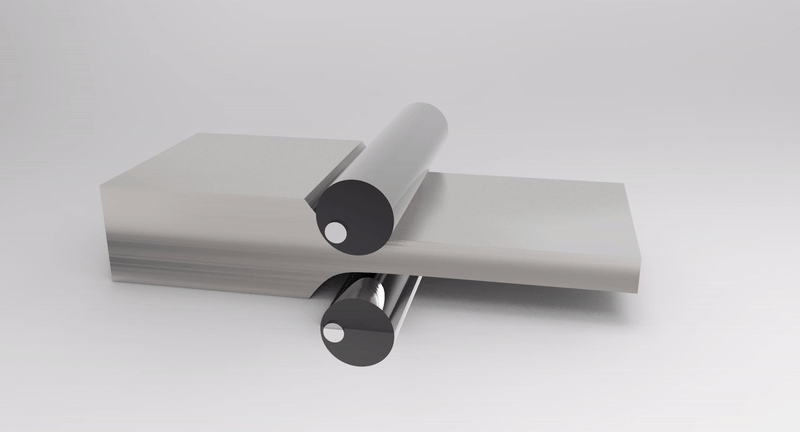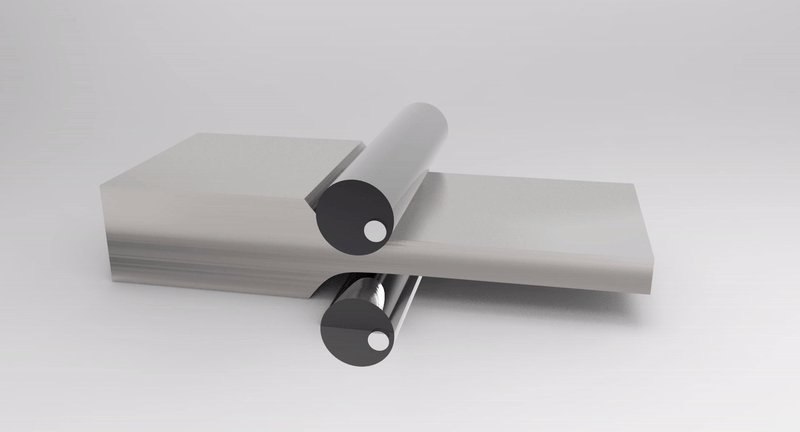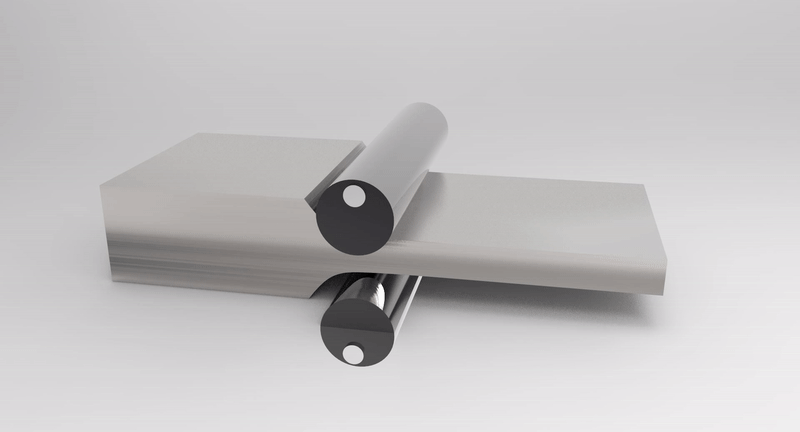
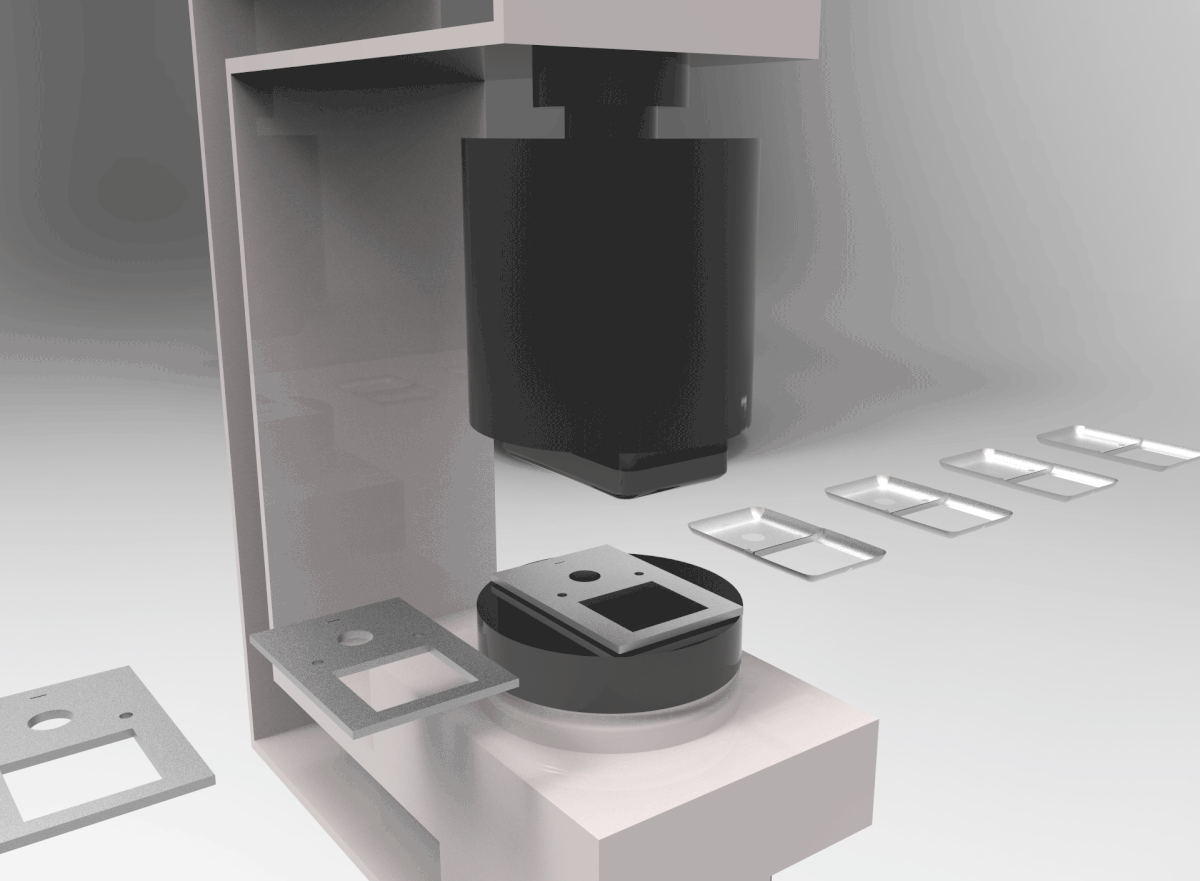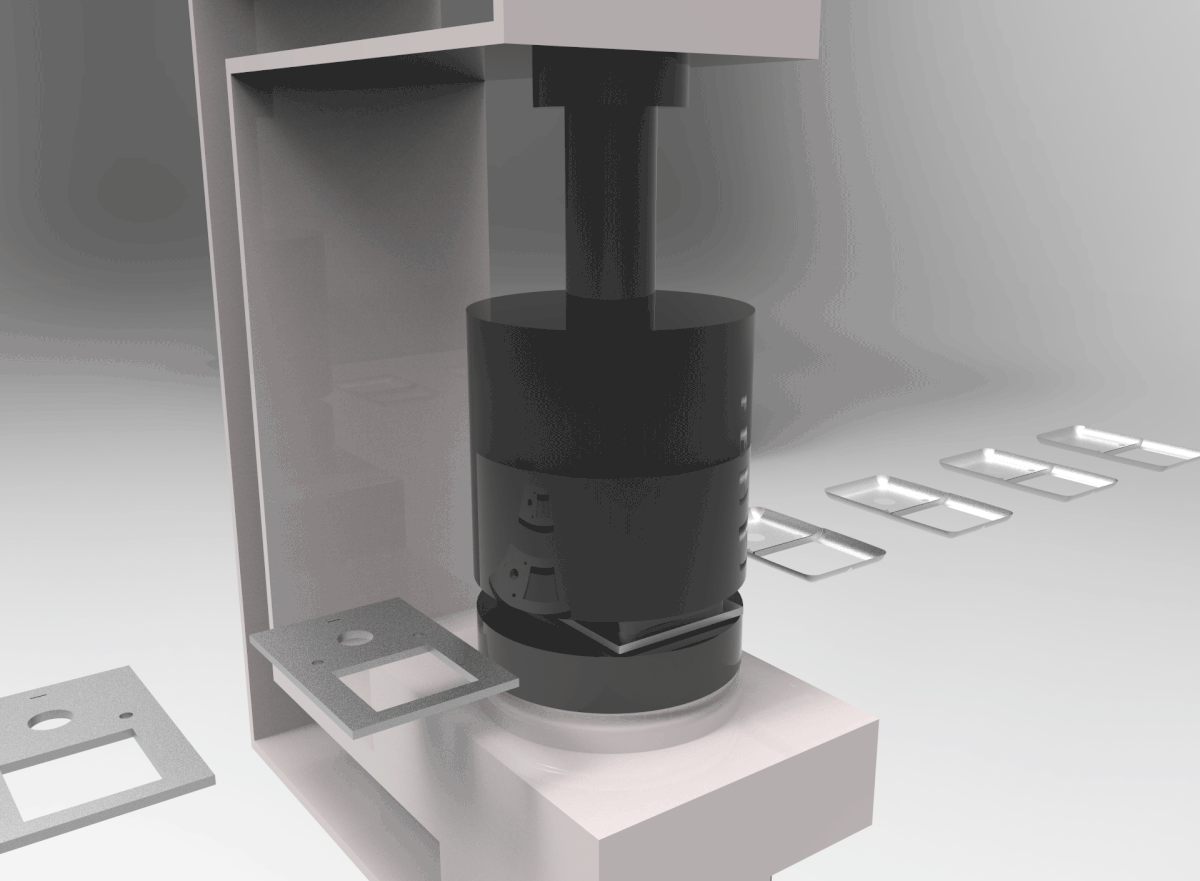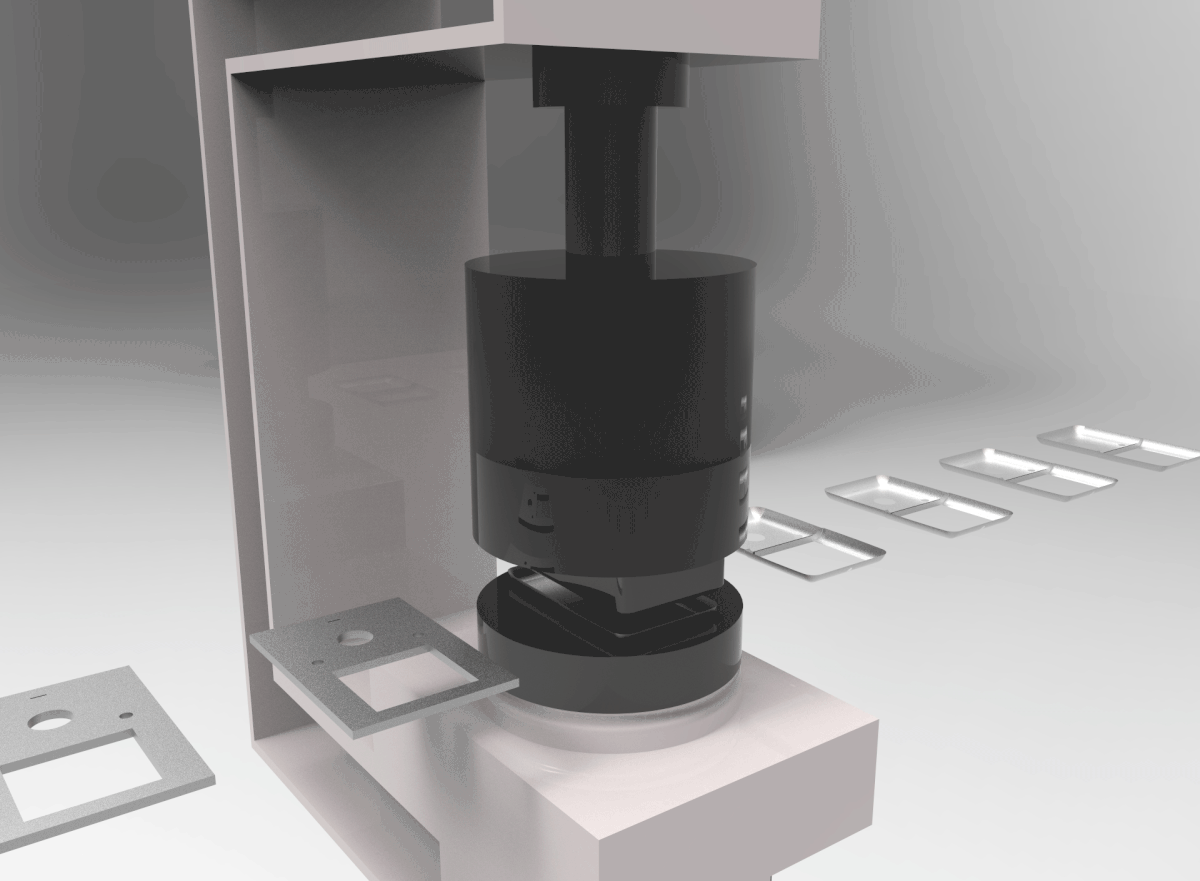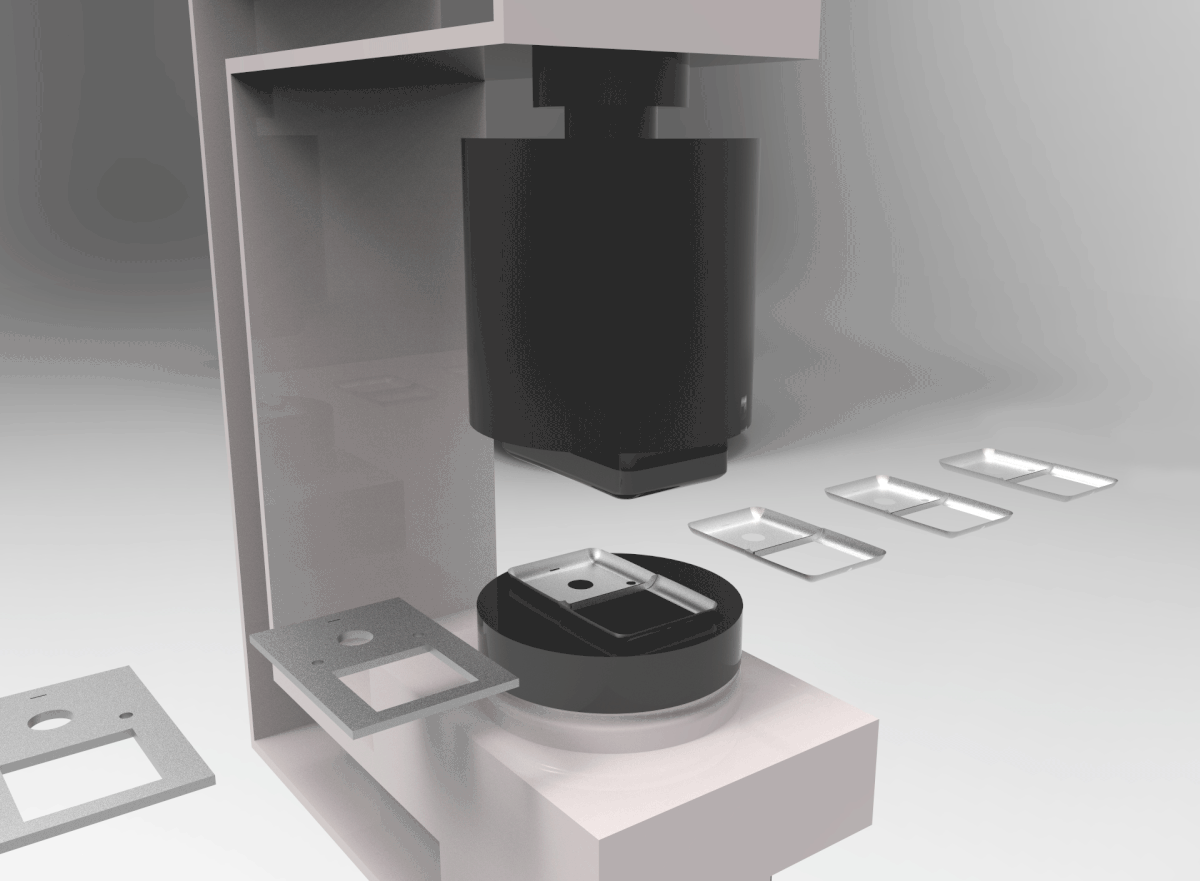
PROCESS 02: Metal Sheet Punching
Punches are of standard geometry. Machines used has to be accurate, fast, and perform rapid tool changes (An example of such machine is the CNC Sheet Metal Machining Centre with limited contouring and forming abilities.)
Why?
Accuracy is important for the different parts to fit properly for the object to function.

PROCESS 03: Continuous Roll Forming
A high-speed process used to produce metal shapes that are somewhat analogous to extrusions except that the profile is limited to the original thickness of the sheet.
Why?
Bending it along one plane is inexpensive and creates simple shapes, giving the sheet rigidity and strength.
PROCESS 04: Thermoplastic Injection Molding
In Injection Molding, melted plastic is forced into a mold cavity. Once cooled, the mold can be removed.
Advantages
Detailed Features, Enhanced strength, Automation (Low labor cost)
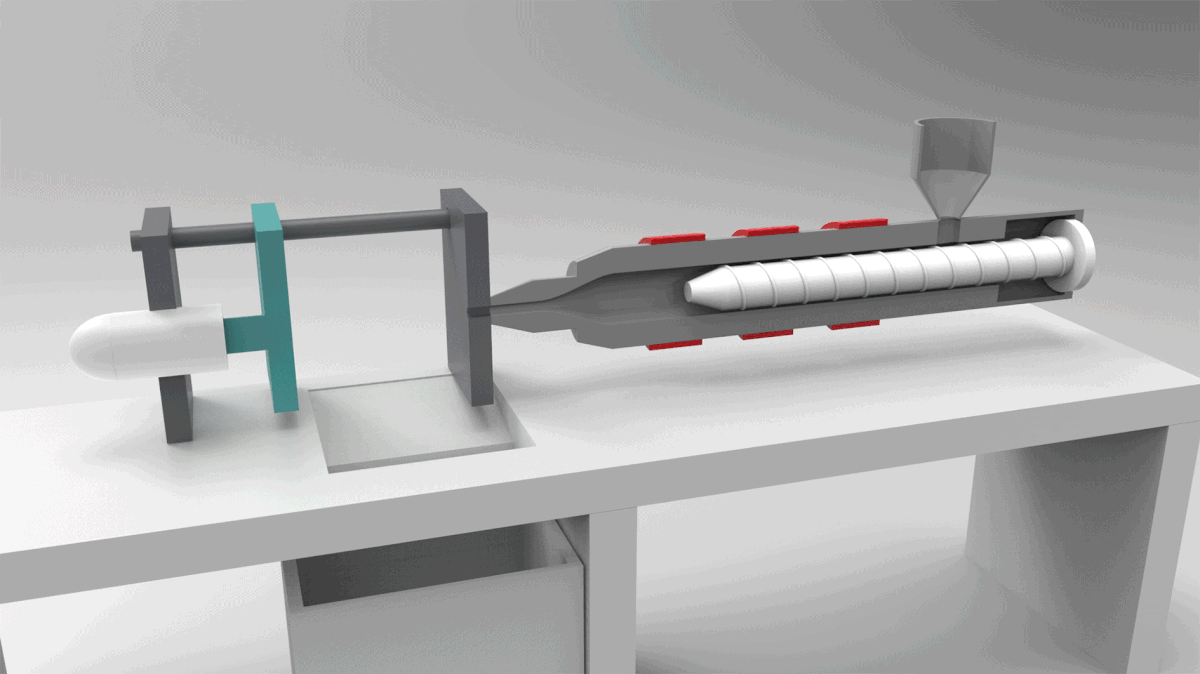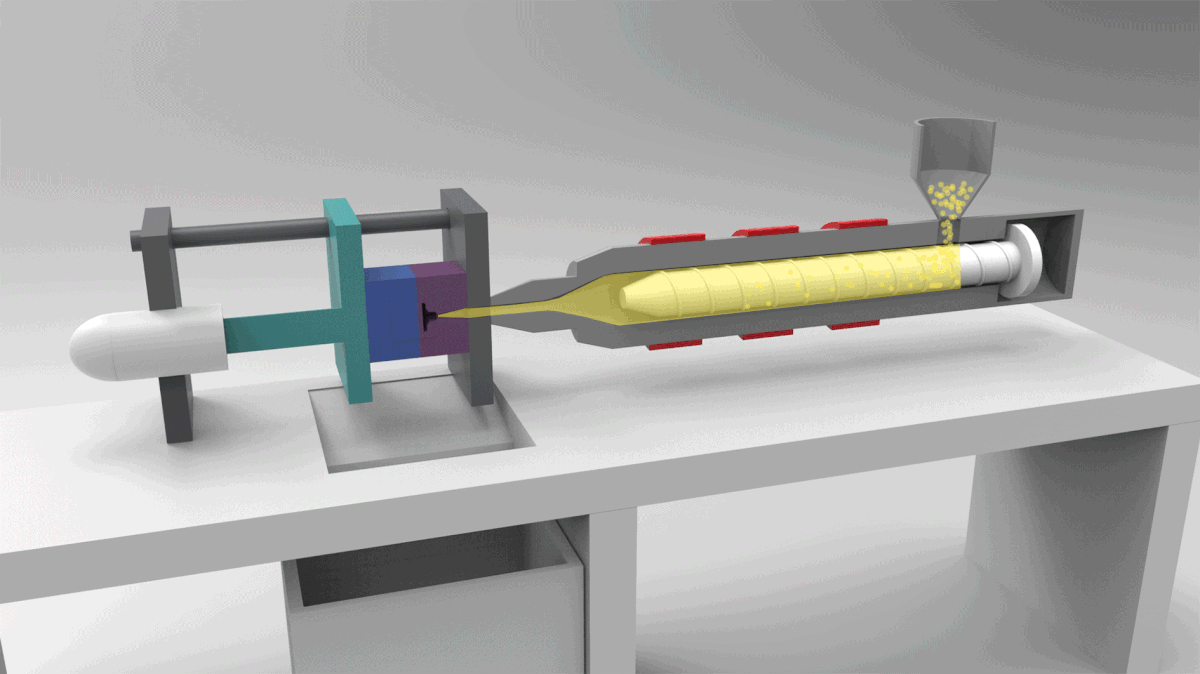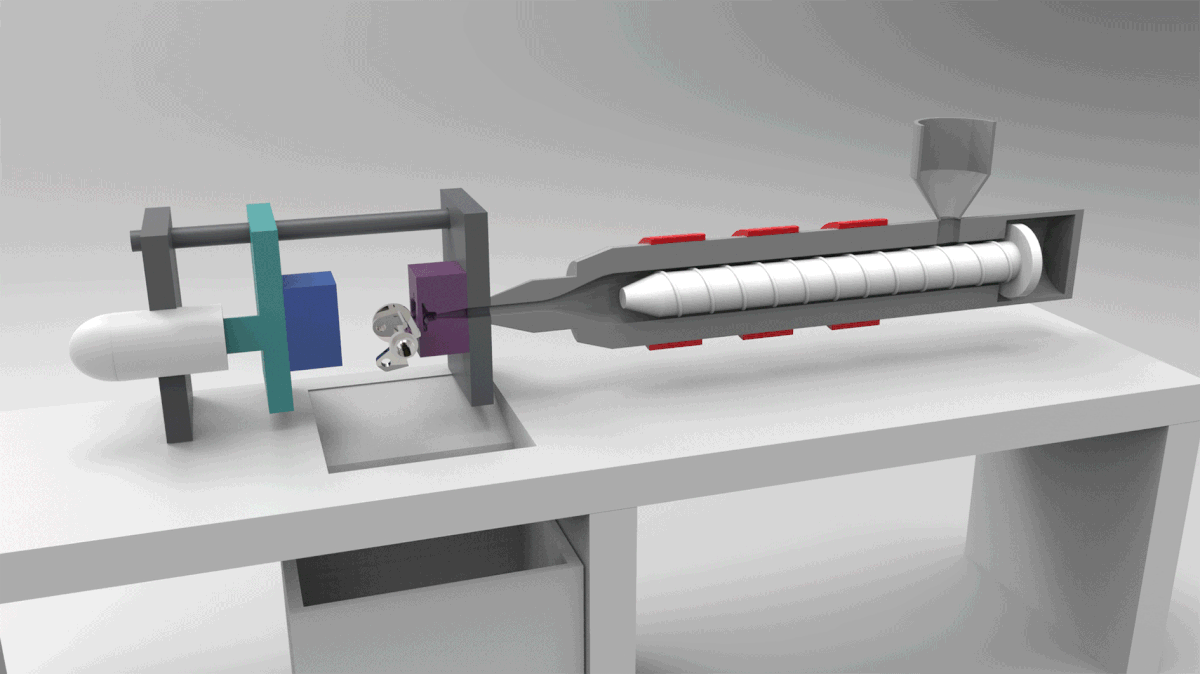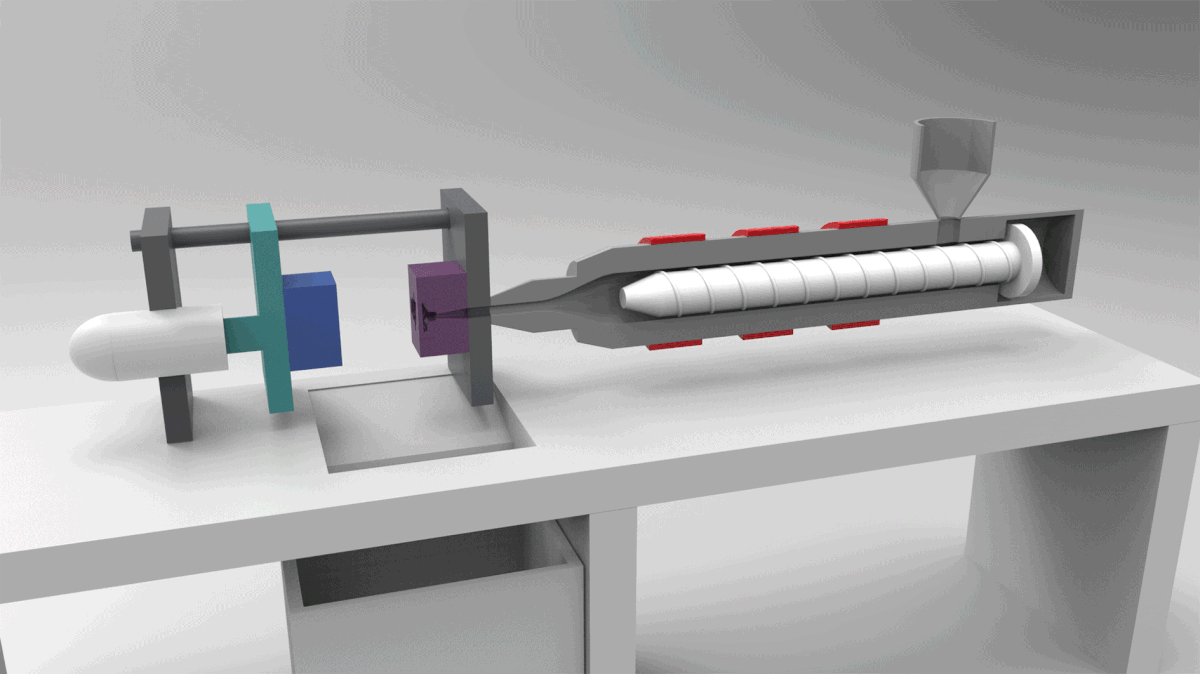
PROCESS 05: Investment Casting
Pattern making - pattern assembly - coating - firing - casting - knockout -finishing




PROCESS 06: Flash Welding
Welding is done through the electrode clamps and the welding transformer

PROCESS 07: Metal extrusion & Cold wiring
Metal extrusion
1. Piece of steel is forced through a die of a smaller cross section area
2. New cross section is formed
Cold wiring
3. The wire is winded around a shaft in room temperature
4. A guiding mechanism (The lead screw on a lathe) is used to align the wire into the desired pitch.
5. Wire is wrapped around the mandrel, coiling it.

PROCESS 08: Chrome Plating
1.The face of the sharpener is immersed in electrolyte.
2. The component(s) to be plated are made of the cathode of the cell - connected to the negative terminal of a low-voltage, heavy current, d.c. supply
3. Anodes are then immersed in the electrolyte and connected to the positive terminal of the supply.
4. Upon the passage of an electric current, metal ions are transferred from the electrolyte onto the surface of the cathode (work) to build up a protective metallic coating.
Advantages
Improved wear and corrosion resistance, improved hardness and durability, bright and appealing metallic finish






Thank you!


